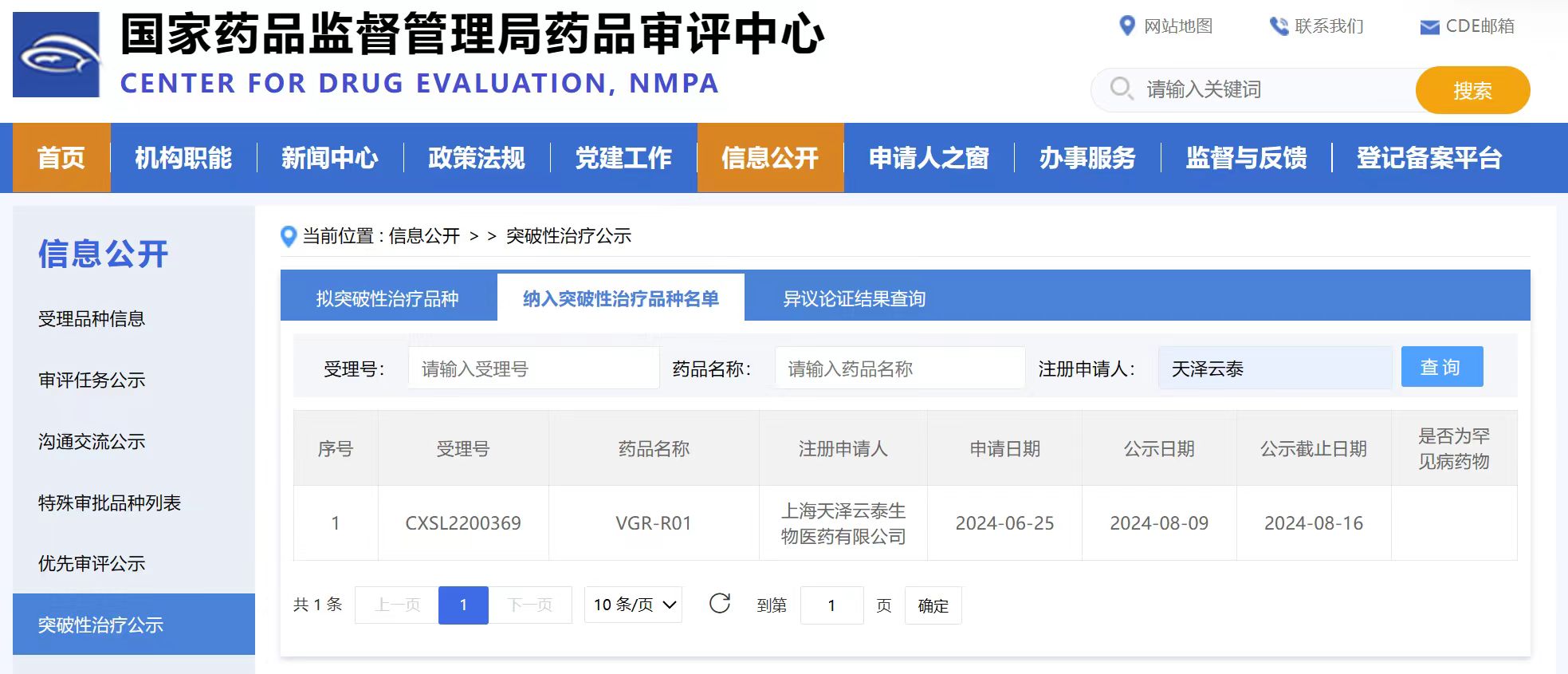
Recently, the official website of the Center for Drug Evaluation (CDE) of the National Medical Products Administration announced that VGR-R01 independently developed by Shanghai Vitalgen BioPharma Co., Ltd. (hereinafter referred to as Vitalgen) was formally included in the list of breakthrough therapeutic varieties for the treatment of bietti crystalline dystrophy (BCD).
Less than 23% of the varieties have been successfully included in the breakthrough therapeutic drug program by the end of 2023 since the implementation of the breakthrough therapeutic drug program application in China. This time, VGR-R01 passed the review by the CDE, who agreed to include it in the breakthrough therapeutic drug program, demonstrating that the use of this product for the treatment of patients with BCD has a clinical significance in terms of important clinical outcomes. This recognition will support and promote the registration and marketing process of this product, marking another important milestone for Vitalgen to move towards commercialization on the path of innovative drug development.
Bietti crystalline corneoretinal dystrophy (BCD) is a progressive retinal degeneration disease with autosomal recessive disorder, first described by Dr. Bietti in 1937. BCD is characterized clinically by shiny yellow-white crystals being deposited in the posterior pole of retina; such yellow-white crystals may appear in the superficial layers of corneal limbus and in circulating lymphocytes, and the disease is accompanied by tapetum retinal degeneration with pigmentation and choroidal sclerosis. Patients with BCD mainly exhibit symptoms such as progressive visual impairment, night blindness, and concentric visual field defects. BCD tends to occur in Asia, especially in China and Japan. A large number of studies have shown that CYP4V2 is the main pathogenic gene of BCD, and the probability of carrying mutation gene related to this disease in Chinese population is approximately 5‰ according to epidemiological statistics. In Europe, the incidence rate of BCD accounts for about 3% of nonsyndromic retinitis pigmentosa and 10% of nonsyndromic autosomal recessive retinitis pigmentosa. There is currently no effective clinical treatment for BCD, and typical RP is mainly referenced, giving supportive therapies such as vasodilators, vitamins, and traditional Chinese medicine treatments. Overseas, it is currently recommended that BCD patients who have progressed to low vision and legal blindness be referred to departments that provide rehabilitation services for visual impairment. Therefore, an effective therapeutic drug is in an urgent need for R&D and marketing.
VGR-R01 is the fastest-progressing innovative drug for gene therapy in the clinical research project of Vitalgen. It is injected into the subretinal cavity and delivers the human CYP4V2 gene to the nucleus through the transduction of retinal pigment epithelial cells (RPE) mediated by AAV capsid protein. The expressed CYP4V2 protein aims to prevent or improve the structural and/or functional damage of RPE cells, photoreceptor cells and choroid by correcting the fatty acid metabolism disorder in the retina of patients, so as to correct visual impairment, protect residual visual function, or delay vision deterioration.
To date, Vitalgen has conducted two clinical studies regarding VGR-R01, where patients with Yuzawa stage 2 or 3 BCD were enrolled, with BCVA of ≤60 ETDRS letters, i.e., ≥0.5 logMAR, and the foveal retinal thickness (CFT) is 96 - 274 μm. The results of both studies indicate that VGR-R01 can be expected to benefit patients with stage 2-3 BCD, including visual acuity enhancement and functional visual improvement, regardless of the presence of retinal chorioretinal atrophy. A multicenter Phase III study is in preparation.