On April 19, 2024, Shanghai Vitalgen BioPharma Co., Ltd., alongside its wholly-owned subsidiary, Shanghai TaiChang Biotechnology Co., Ltd. (hereinafter referred to as the “Company”), received the Green Light from the National Medical Products Administration (NMPA) to embark on clinical trials for their groundbreaking gene therapy drug VGN-R09b. The drug, developed and manufactured entirely in-house, targets the treatment of primary Parkinson’s disease (PD) and aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase deficiency (AADCD).
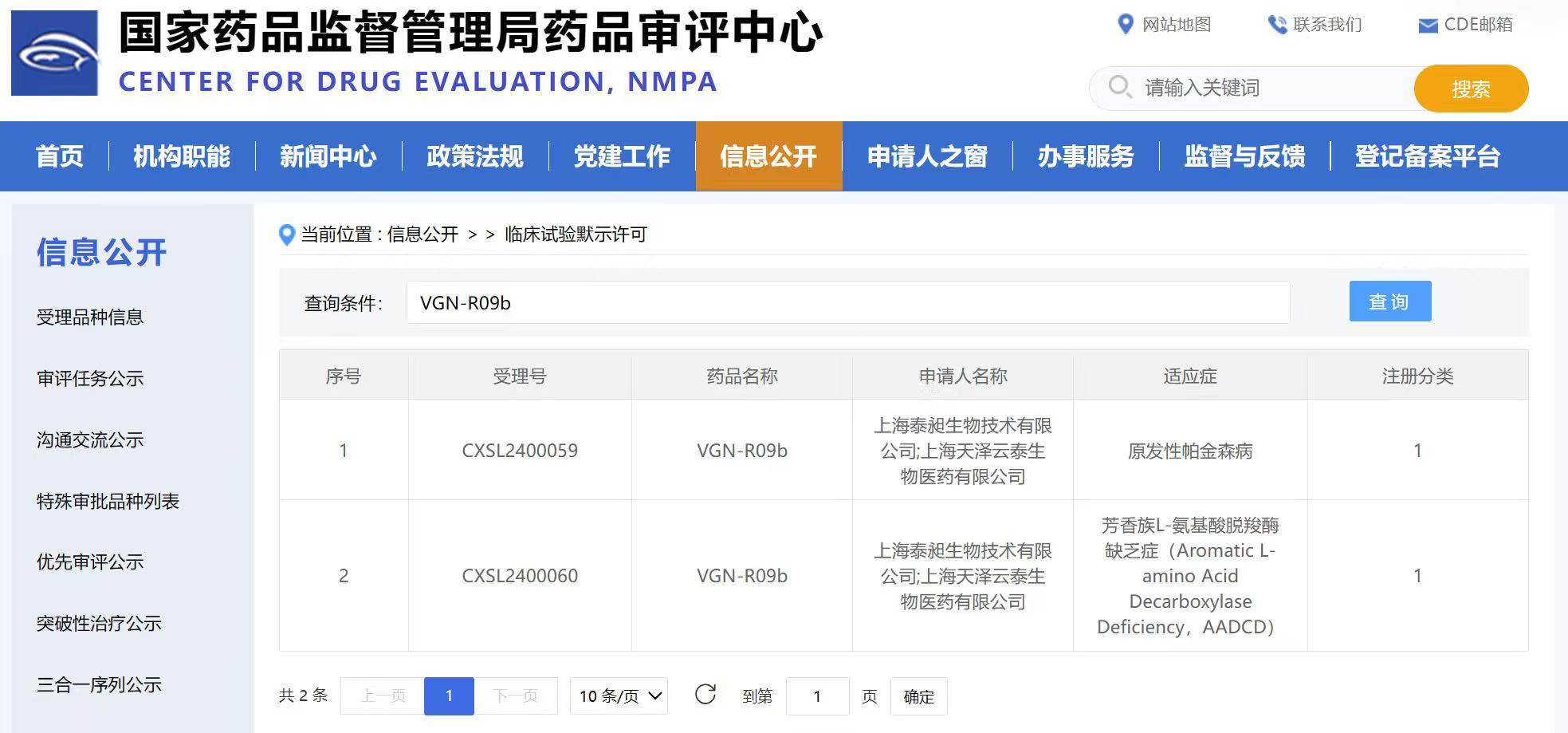
VGN-R09b holds the distinction of being China’s pioneering gene therapy to secure clinical trial approval by deploying an innovative AAV-based dual-gene delivery strategy. This remarkable milestone not only signifies its transition from treating rare diseases to tackling common ailments but also exemplifies the Company’s steadfast dedication to revolutionizing medical treatments.
Dr. Zhao Xiaoping, the Company’s Chairman, expressed his elation, stating, “The NMPA’s green signal for conducting simultaneous clinical trials of VGN-R09b in two distinct indications underscores their confidence in its safety, potential benefits, and product quality for the targeted patient population. With its sterling safety record and unparalleled efficacy, we anticipate VGN-R09b to positively impact the lives of countless patients.”
About Parkinson's Disease
Parkinson's disease (PD) is the second most common neurodegenerative disease, and the prevalence of Parkinson's disease is increasing faster than many other neurodegenerative diseases. Parkinson's disease is estimated to affect about 1% of the population over the age of 65 and 4% of those over the age of 85. The prevalence of people over 65 years old in China was 1.7%, which was similar to that of European and American countries. In the future, the number of patients with Parkinson's disease in China will rise from 1.99 million in 2005 to 5 million in 2030, accounting for almost half of the number of Parkinson's patients around world.
About AADC Deficiency
Aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase (AADC) deficiency is caused by a pathogenic mutation in the DDC gene encoding AADC, which is responsible for the decarboxylase of L-DOPA (levodopa) and 5-HTP (5-hydroxytryptophan) to form the neurotransmitters dopamine and 5-hydroxytryptamine, respectively. AADC deficiency impedes the synthesis of critical neurotransmitters that control the sympathetic nervous system, emotion, cognition and motor coordination, presenting clinical symptoms such as motor dysfunction, mental retardation and diminished alertness and sleep disturbances, with a risk of premature death in the first decade of life. There are no formal epidemiological studies of the disease in China except a newborn screening program for AADC deficiency in Taiwan, which showed a birth incidence of AADC deficiency of approximately 1/32,000.
About VGN-R09b
VGN-R09b is a gene therapy product independently developed and manufactured by Vitalgen BioPharma, which uses recombinant AAV as a gene therapy vector to recover dopamine production based on the delivery of functional AADC, thus playing the corresponding potential therapeutic effects. By local striatal injection, the drug can be applied directly to the site of disease, reducing the dose administered systemically and correspondingly leading to a decrease in adverse effects such as immune reactions. Theoretically, gene therapy requires only one injection to have long-term therapeutic effects.